Page 74 - New Grammar with a Smile 8
P. 74
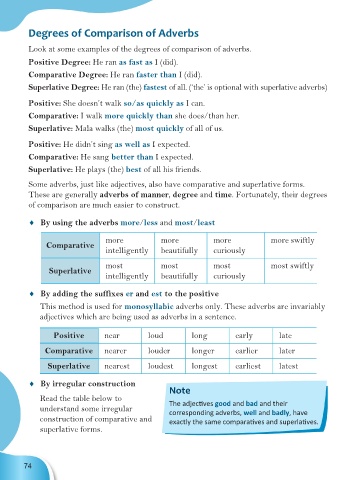
Degrees of Comparison of Adverbs
Look at some examples of the degrees of comparison of adverbs.
Positive Degree: He ran as fast as I (did).
Comparative Degree: He ran faster than I (did).
Superlative Degree: He ran (the) fastest of all. (‘the’ is optional with superlative adverbs)
Positive: She doesn’t walk so/as quickly as I can.
Comparative: I walk more quickly than she does/than her.
Superlative: Mala walks (the) most quickly of all of us.
Positive: He didn’t sing as well as I expected.
Comparative: He sang better than I expected.
Superlative: He plays (the) best of all his friends.
Some adverbs, just like adjectives, also have comparative and superlative forms.
These are generally adverbs of manner, degree and time. Fortunately, their degrees
of comparison are much easier to construct.
♦ By using the adverbs more/less and most/least
more more more more swiftly
Comparative
intelligently beautifully curiously
most most most most swiftly
Superlative
intelligently beautifully curiously
♦ By adding the suffixes er and est to the positive
This method is used for monosyllabic adverbs only. These adverbs are invariably
adjectives which are being used as adverbs in a sentence.
Positive near loud long early late
Comparative nearer louder longer earlier later
Superlative nearest loudest longest earliest latest
♦ By irregular construction
Note
Read the table below to The adjectives good and bad and their
understand some irregular corresponding adverbs, well and badly, have
construction of comparative and exactly the same comparatives and superlatives.
superlative forms.
74