Page 114 - New Grammar with a Smile 5
P. 114
Comparison
24
of Adverbs
You have learnt that adjectives have three degrees of comparison. Like adjectives,
adverbs too have three degrees—the positive, the comparative and the superlative.
For example,
y Ravi works hard. (positive)
y Praveen works harder than Ravi. (comparative)
y Syed works the hardest of all. (superlative)
Let us now study how adverbs form their comparatives and superlatives.
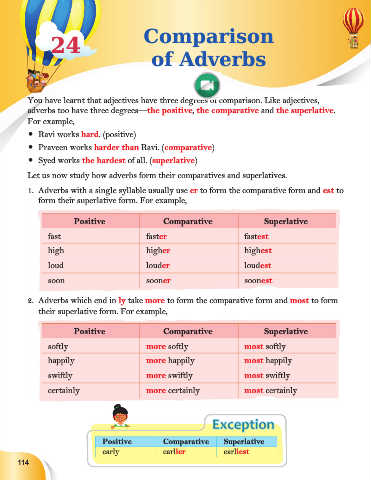
1. Adverbs with a single syllable usually use er to form the comparative form and est to
form their superlative form. For example,
Positive Comparative Superlative
fast faster fastest
high higher highest
loud louder loudest
soon sooner soonest
2. Adverbs which end in ly take more to form the comparative form and most to form
their superlative form. For example,
Positive Comparative Superlative
softly more softly most softly
happily more happily most happily
swiftly more swiftly most swiftly
certainly more certainly most certainly
Exception
Positive Comparative Superlative
early earlier earliest
114