Page 50 - New Grammar with a Smile 7
P. 50
Degrees of Adjectives
You have learnt that there are three degrees of adjectives—positive, comparative
and superlative.
1. Positive degree: When we talk about the existence of some quality in a person or
a thing, we use the positive degree. For example,
y Sushma is a tall girl.
y Vasanthi is an intelligent girl.
2. Comparative degree: When we compare two people or things, we use the
comparative degree. For example,
y Parul is taller than Sushma.
y Jaya is more intelligent than Vasanthi.
3. Superlative degree: When we compare three or more people or things, we use
the superlative degree. For example,
y Sukanya is the tallest of all.
y Sonali is the most intelligent of all.
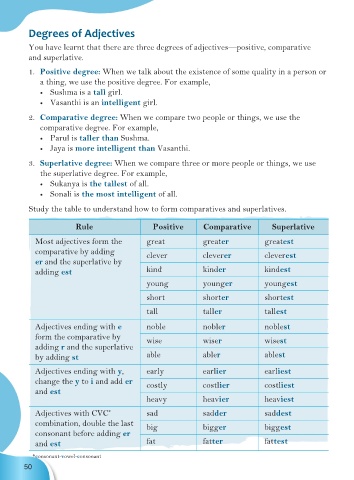
Study the table to understand how to form comparatives and superlatives.
Rule Positive Comparative Superlative
Most adjectives form the great greater greatest
comparative by adding clever cleverer cleverest
er and the superlative by
adding est kind kinder kindest
young younger youngest
short shorter shortest
tall taller tallest
Adjectives ending with e noble nobler noblest
form the comparative by wise wiser wisest
adding r and the superlative
by adding st able abler ablest
Adjectives ending with y, early earlier earliest
change the y to i and add er costly costlier costliest
and est
heavy heavier heaviest
Adjectives with CVC sad sadder saddest
*
combination, double the last big bigger biggest
consonant before adding er
and est fat fatter fattest
*consonant-vowel-consonant
50