Page 55 - New Grammar with a Smile 7
P. 55
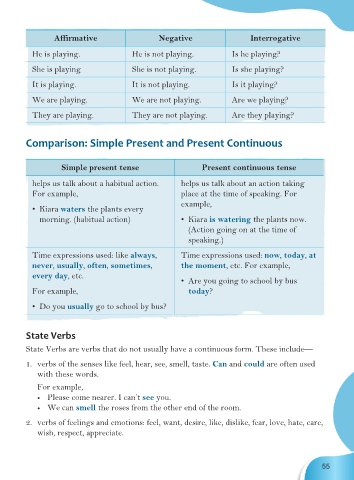
Affirmative Negative Interrogative
He is playing. He is not playing. Is he playing?
She is playing She is not playing. Is she playing?
It is playing. It is not playing. Is it playing?
We are playing. We are not playing. Are we playing?
They are playing. They are not playing. Are they playing?
Comparison: Simple Present and Present Continuous
Simple present tense Present continuous tense
helps us talk about a habitual action. helps us talk about an action taking
For example, place at the time of speaking. For
example,
• Kiara waters the plants every
morning. (habitual action) • Kiara is watering the plants now.
(Action going on at the time of
speaking.)
Time expressions used: like always, Time expressions used: now, today, at
never, usually, often, sometimes, the moment, etc. For example,
every day, etc.
• Are you going to school by bus
For example, today?
• Do you usually go to school by bus?
State Verbs
State Verbs are verbs that do not usually have a continuous form. These include—
1. verbs of the senses like feel, hear, see, smell, taste. Can and could are often used
with these words.
For example,
y Please come nearer. I can’t see you.
y We can smell the roses from the other end of the room.
2. verbs of feelings and emotions: feel, want, desire, like, dislike, fear, love, hate, care,
wish, respect, appreciate.
55