Page 60 - New Grammar with a Smile 8
P. 60
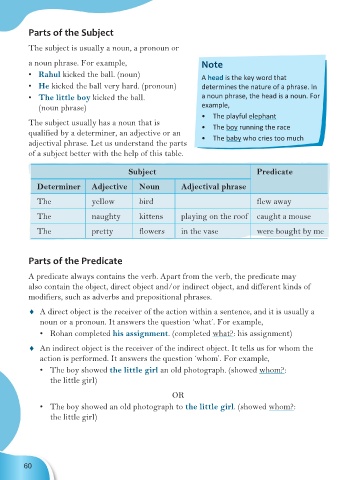
Parts of the Subject
The subject is usually a noun, a pronoun or
a noun phrase. For example, Note
• Rahul kicked the ball. (noun) A head is the key word that
• He kicked the ball very hard. (pronoun) determines the nature of a phrase. In
• The little boy kicked the ball. a noun phrase, the head is a noun. For
(noun phrase) example,
• The playful elephant
The subject usually has a noun that is • The boy running the race
qualified by a determiner, an adjective or an • The baby who cries too much
adjectival phrase. Let us understand the parts
of a subject better with the help of this table.
Subject Predicate
Determiner Adjective Noun Adjectival phrase
The yellow bird flew away
The naughty kittens playing on the roof caught a mouse
The pretty flowers in the vase were bought by me
Parts of the Predicate
A predicate always contains the verb. Apart from the verb, the predicate may
also contain the object, direct object and/or indirect object, and different kinds of
modifiers, such as adverbs and prepositional phrases.
♦ A direct object is the receiver of the action within a sentence, and it is usually a
noun or a pronoun. It answers the question ‘what’. For example,
• Rohan completed his assignment. (completed what?: his assignment)
♦ An indirect object is the receiver of the indirect object. It tells us for whom the
action is performed. It answers the question ‘whom’. For example,
• The boy showed the little girl an old photograph. (showed whom?:
the little girl)
OR
• The boy showed an old photograph to the little girl. (showed whom?:
the little girl)
60